Macro Molecules:
Macro Molecules, are large molecules, made by joining together of many small molecules.
This process of joining together smaller units into a large macro molecule polymer is called polymerization.
Monomer:
Small molecules, that join together to form one large polymer molecules.
There are two kinds of polymer:
Synthetic Polymer
Natural Polymers
Synthetic Polymers:
Synthetic Polymers are manmade polymers that are formed by
- Addition Polymerization – Addition Polymers
- Condensation Polymers – Condensation Polymers
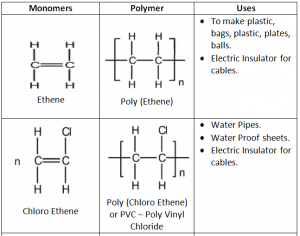
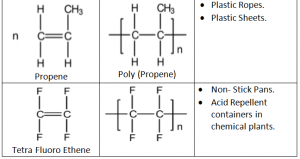
Addition Polymers:
Addition Polymers are made from unsaturated monomers through an addition reaction.
Repeating Unit: Simplest part of the polymer which is repeated many times to form the polymer.
In addition Polymerization any alkene is converted into Poly alkene.
Alkane is converted to Alkane.
Making of Poly Ethene conditions:
Temperature – 200 °C
Atmospheric Pressure: 1000
Catalyst – Zeigler’s Catalyst – TiCl4 + (C2H5)3 Al – Mixture of Titanium Tetre Chloride and Tetra Aluminium
Further Advantages of Addition Polymerization:
Perspex – Used in making car windows
Taflon – Used in production of utensils, rain coats and rubber tubings
Polystylene – Disposable glasses and plastics.
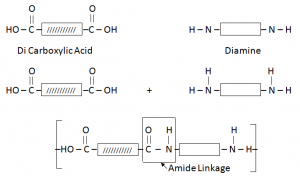
Condensation Polymers:
When two different monomers join, each with two functional group. The monomers join their functional groups, by getting rid of or eliminating small molecules.
Condensation Polymers are made from monomers containing alcohol, acid or amino functional groups.
Through elimination of small molecules like H2O. E.g. Nylon and Teryline.
Nylon/ Polyamide:
It is formed by the combination of Di Carboxylic Acid and Di Amine.
- Why Nylon also called as Poly Amide – due to presence of Amide Linkage.
Uses of Nylon:
- Nylon is used in making synthetic fibres
- In production of ropes, fishing lines and clothes
- For making rain coats and parachutes.
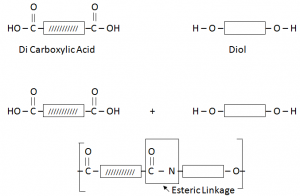
Terylene / Polyester:
Terylene is formed by the combination of DiCarboxylic Acid and Diol (Hydroxyl Group).
Uses of Terylene:
- Fabrics – That are strong, resists strechingand sinking. Doesn’t crumple.
- Sleeping bags are made using teryline. Hence they do not shrink (Synthetic Fibre).
Disadvantages of Plastic:
- Plastics are non-biodegradeble, can’t be decomposed by bacteria. Hence they result in polluting the earth.
- Produce toxic gases(HCl) when burnt, this contriburtes to acid rain.
- Plastics are Carbon based polymers – burn easily.
- Plastics that require Chloro-Flouro Carbons (CFC) during production may contribute to global warming when the CFC is allowed to escape. Thus may lead to flodding in low lying areas.
Natural Polymers:
Natural Polymers are formed by condensation polymerization.
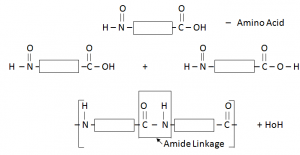
Protein:
When two amino acids combine with each other, protein is formed and H2O is a by-product.
Protein have similar linkage to that of Nylon (amide linkage) –Thus can be called Polyamide.
They are joined together by condensation polymerization.
Each amino acid has an acidic functional group and an amino functional group.
Proteins are possessing the same amide linkages as Nylon but with different monomer units.
Proteins can also by hydrated back into amino acids, by heating them with Sulphuric Acid (H3PO4).
Hydrolysis:
Is a reaction in which molecules are broken down by reaction with water, in the presence of Alkali or Acid.
The products of the hydrolysis of protein (amino acids) and Carbohydrates can be separated and identifies through chromatography.
The chromatogram needs to be sprayed with a locating agent (Ninhydrin) so that they can become visible and be compared to other pure samples of the monomer.
Carbohydrates:
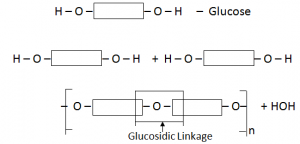
Carbohydrates are polymers made up of small sugar molecules joined together e.g. starch.
Carbohydrates contain Carbon, Hydrogen and Oxygen.
General Formula: CnC(H2O)n
Simplest Carbohydrate C6H12O6 (Glucose)
Glucose polymerise each other to form starch
Equation:
C6H12O6  (C5H10O5)n + nH2O
(C5H10O5)n + nH2O
Hydrolysic of Carbohydrates to convert them to simple sugar:
Starch can be broken down to glucose (Simple Sugar molecules by heating with Sulphuric Acid (Hydrolysis) – H2O molecule is added.
Chromatography can be used to identify small molecules of sugar
Fats:
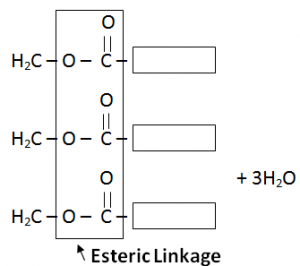
Fats are formed through condensation reaction of fatty acids (Carboxylic Acids) and Glycerol (3 Carboon atom chains having OH attached with every Carbon atom).
H2O is also a by – product.
Fat is formed as a single large molecule so no need to write continuation brackets.
Glycserol contains three – OH functional groups per molecule and is hence known as a triol.
Each molecule of glycerol will combine with three molecules of fatty acids and form one molecule of fat.
Fats have same esteric linkages as Terylene (also known as polyster).
Fats can also be broken down to sodium salts of fatty acids and glycerol by boiling it with Acid or Alkalis (Hydrolysis).


No comments:
Post a Comment