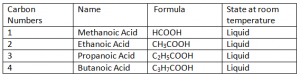
Carboxylic Acids:
Carboxylic Acids are homogenous Series/ organic compounds containing the (CO2H) group.
General Formula: CnH2n + 1 COOH
Carboxylic Acids are not HydroCarbons, as they contain Oxygen in their Compounds. Hydro Carbonds are those organic compounds containing only Hydrogen and Carbon.
Properties Of Carboxyic Acids:
- All of them are 100% soluble in water.
- Chemical reaction of Carboxylic Acids are dependent upon C = O (Carboxyl) and H = O (Hydroxyl).
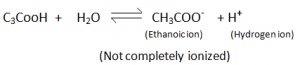
- They are weak acids (partially ionizes in water).
i.e. weaker than inorganic acids – inorganic compounds completely ionize hence more reactive than carboxylic acids.
In Organic Acid:
Organic Acid:
- Carboxylic Acids are partially ionized, to give Hydrogen ions in H2
- They dissacociate only partially in water to form hydrogen ions.
Reactions With Metals:
Reactions With Carbonates + Bi Carbonates:
Reactions With Basis:
Production Of Ehtanoic Acid (Carboxylic Acid):
Ethanoic Acid is dropped by the oxidation of Ethanol.
- Using Atmospheric Oxygen:
- By the oxidation of Ethanol in fermented solution with atmospheric oxygen in the presence of certain bacteria.
- When ethanol is left standing in air, bacteria bring about its oxidation to Ethanoic acid – acid fermentation.
- Acid fermentation is used to make vinegar (a dilute solution of Ethanoic acid.) The vinegar is produced from foods such as apples, rice and honey which are first fermented to give ethanol.
C2H5OH(l) + O2(g) CH3COOH(l) + H2O(l)
- Using Oxidizing Agents:
- By heating Ethanol with an oxidizing agent such ad acidified Potassium Dichromate(VI) (K2Cr2o7).
- Ethanol is oxidized much faster by warming the oxidizing agent K2Cr2o7 in the presence of an acid.
- K2Cr2o7 produces atomic Oxygen which more reactive than normal Oxygen (O).
- The Orange K2Cr2o7 solution changes its colour to Green.
- H2O is also produced as a byproduct while producing ethanol.
Esterification:
Esters are organic compounds formed by the combination of Carboxylic Acis with an Alcohol.
Catalyst – Concentrated Sulphuric Acid (H2SO4)
This Reaction is reversible.
H20 is produced as a by – product.
Ester is a sweet smelling organic compound.
Preperation of Ester is known as esterification.
We can add Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH) and heat mixture to obtain Carboxylic acid and alcohol from ester – This is Hydrolysis.
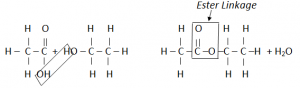
OH – from acid H from alcohol – Ester formation
The two functional groups react with each other. The C of the Carboxyl group bonds to the O of the OH group. The COO group where they join is called ester linkage.
The two molecules have joined by getting rid of a small molecule, water. This is called condensation reaction.
In Condensation reaction, two molecules join together to form a large molecule, with the loss of a small molecule.
Uses of Esters:
- As a flavouring agent in foods.
- Used in cosmetics.
- Used as a solvent, to dissolve organic compounds that are insoluble in wate. They are volatile, hence they evaporate easily. (painting, ink, glues and nail polish).
- Esters are used in creating vegetable oils.
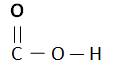
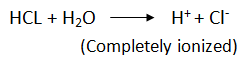
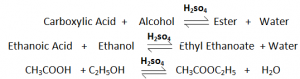
No comments:
Post a Comment